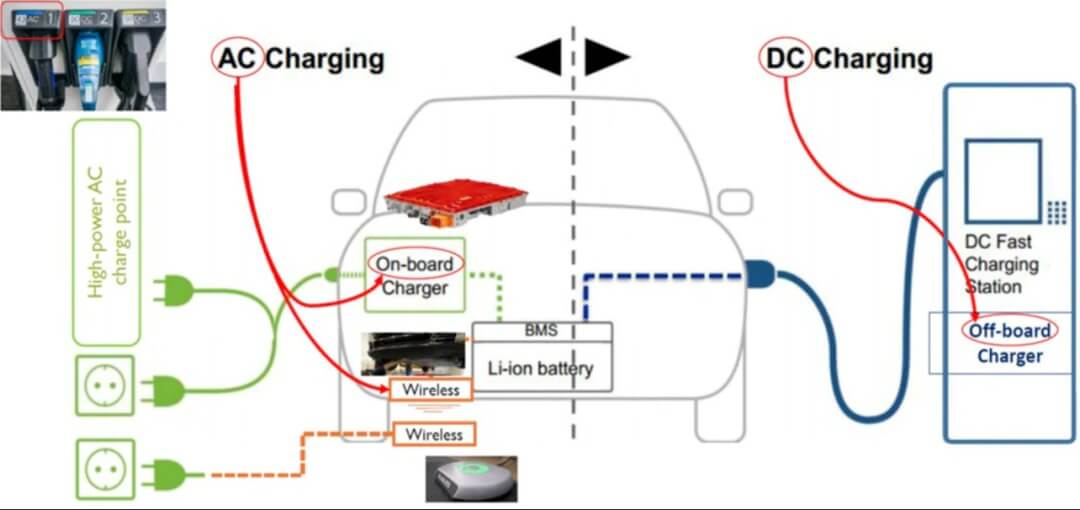
With the rapid development of electric vehicles (ЕВ), charging technology has become a focus of our’s attention. Among them, Зарядные устройства для электромобилей переменного тока и DC Fast Chargers are the two most common and familiar types. What is the difference between the two and how to choose? This article will deeply analyze the core differences between the two to help us make the right choice.

Charging Principles:
AC chargers (AC charging): The alternating current (переменного тока) provided by the power grid is transmitted to the vehicle through the charging pile, and then converted to direct current (ОКРУГ КОЛУМБИЯ) by the on-board charger (OBC) and stored in the battery.
Power range: Usually 7-22 кВт, suitable for slow charging at home and in public places.
Charging time: Fully charged takes 4-12 часы, depending on the battery capacity and charging power.
DC Fast Chargers (DC fast charging): The charging pile has a built-in converter that directly converts AC to DC, bypassing the on-board charger and directly supplies power to the battery.
Power range: 50 кВт это 350 кВт (some supercharging can reach 1.5 MW), and can be charged to 80% в 30 минуты.
Charging time: 200 kilometers of range in as fast as 10 минуты (such as BYD megawatt supercharging)
Use Cases:
| Scenario | AC Charger | Быстрое зарядное устройство постоянного токас |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Office | Ideal for overnight charging | Impractical (high grid demand) |
| Long-Distance Travel | Limited range replenishment | Highway rest stops, rapid charging |
| Public Parking | Widely available for daily use | Concentrated in hubs, malls |
Technical Compatibility:
- Connector Types:
- переменного тока: Тип 1 (US), Тип 2 (EU), ГБ/Т (Китай).
- ОКРУГ КОЛУМБИЯ: CCS (EU/US), ЧАдеМО (Japan), or Tesla Supercharger.
- Vehicle Limits: Most plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) lack DC fast-charging support.
Pros and Cons Analysis:
AC Charger: Strengths and Limitations
- Pros:
- Affordable, ideal for residential use.
- Gentler on battery longevity.
- Cons:
- Slow charging, unsuitable for emergencies.
DC Fast Chargers: Strengths and Limitations
- Pros:
- Ultra-fast charging for long trips.
- Future-proof with high-power support (например, 350+ кВт).
- Cons:
- Frequent use may accelerate battery degradation (~0.1% added wear).
- Higher public charging costs and infrastructure dependency.
How to Choose?
1. Which is better for daily commutes?
Choose AC charging for cost efficiency and battery health.
2. Does DC fast charging harm batteries?
Modern EVs manage heat effectively—occasional use has negligible impact.
3. Will AC chargers become obsolete?
Нет. AC remains essential for daily needs, while DC evolves toward megawatt speeds (например, Huawei’s 1.5 MW chargers).